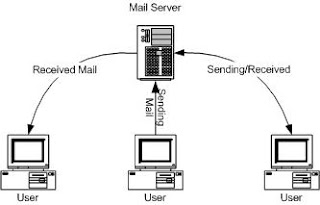
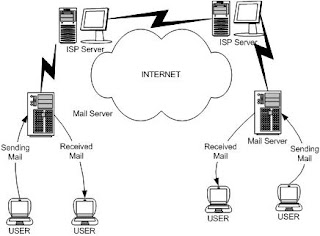
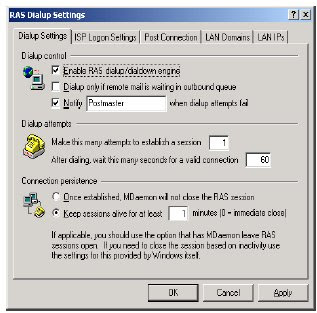
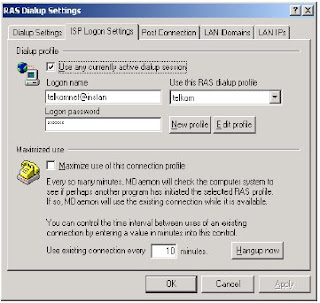
Denial of Service (DoS)
- This type entangling the hacker and or a certain party to send a number of ICMP echo request to the broadcast address. Remember that the address of sender request have been disguised so difficult to tracks.
- Protection to the network can be done by selection to the reciprocation of ICMP echo, another way is do not activate the directed broadcast at the router. Permit out package only and the sender address same with internal network address. This is important to the network security
- The other level of Denial of Service(DoS) is Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS).
This type will increase the traffic and combine the bandwidth from some of host to one target host or network.
- Is the creation of TCP/IP packets using somebody else's IP address. Routers use the "destination IP" address in order to forward packets through the Internet, but ignore the "source IP" address. That address is only used by the destination machine when it responds back to the source.
- By using broadcast amplification, an attacker can direct machines at one site to flood another site with network packets. If huge amounts of packets are sent to a site, it goes down under the load, causing denial of service. To prevent this technique from being used, the document's authors suggest that companies turn off the capability to forward directed broadcast or multicast traffic.
- is an attack based on bogus TCP connection requests, created with a spoofed source IP address, sent to the attacked system. Connections are not completed, thus soon it will fill up the connection request table of the attacked system, preventing it from accepting any further valid connection request.
The source host for the attack sends a SYN packet to the target host. The target hosts replies with a SYN/ACK back to the legitimate user of the forged IP source address.
Since the spoofed source IP address is unreachable, the attacked system will never receive the corresponding ACK packets in return, and the connection request table on the
Attacked system will soon be filled up.The attack works if the spoofed source IP address is not reachable by the attacked system. If the spoofed source IP address where reachable by the attacked system, then the legitimate owner of the source IP address would respond with a RST packet back to the target host, closing the connection and defeating the attack.
TCP SYN flood is a denial of service attack that sends a host more TCP SYN packets than the protocol implementation can handle.
This is a resource starvation DoS attack because once the connection table is full, the server is unable to service legitimate requests.