 MDaemon is one of the utilized software as server mail besides other mail server software.
MDaemon is one of the utilized software as server mail besides other mail server software.Hardware requirement for MDaemeon as a Mail Server is :
Service E-Mail Protocol
- There are two protocol which often use in E-mail service as a main protocol:
- Simple Mail transfer protocol (SMTP)
- Post Office Protocol Version 3 (POP3
Besides the protocol above, also recognized Internet Mail Access Protocol ( IMAP ) which its function like POP3 with a few excess. Following will be explained function and way of activity for each protocol (See my previous posted about the protocol).
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Main function of SMTP is to submit E-Mail from a host to other host in network. This protocol do not have ability to conduct depository and intake of E-Mail from a Mailbox. TCP port protocol for SMTP service is 25, representing service standard port SMTP. Because SMTP do not have depository ability in mailbox E-mail, hence needed other protocol to run the function that is POP3 and IMAP.
- From E-Mail client side, SMTP server represent medium to conduct connection outgoing or delivering message. While for the incoming of connection used by POP3 protocol.
Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3)
Version 3 is a POP Protocol, more popular as a POP3 in this time. This protocol function is to get E-Mail in mailbox for every user in server mail, what usually also function at the same time as a SMTP server. As have been explained previously that SMTP do not have depository mechanism of E-Mail to mailbox and distributing it every user, so that POP3 protocol to take the function. POP3 server keep the E-Mail of every user for temporary before finally download by user use E-Mail client like Outlook and also Eudora. In course of the intake of E-Mail Client Connected to the Mail server use POP3 protocol at TCP port 110.
Function of DNS server in Email service
In E-Mail DNS server service personate indicator to the route an E-Mail. If there are an E-Mail, DNS server will check the name of domain that found on address of target.
E-Mail service in LAN environment generally aim to facilitate coordination between internal of an organization. The Scope of LAN in fact can be extended in WAN scale. This mode is not used public network or Internet.
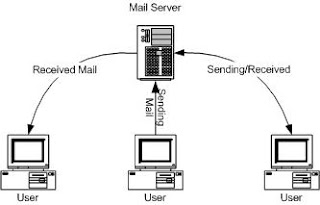
Email service in WAN
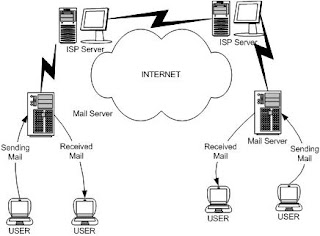
Setting MDaemon at LAN
- MDaemon can be used at LAN to send and received an E-mail like Email via WAN.
- Make Domain at Local Network
- Make Account and Mailbox each user
- Configure E-Mail client each user
There are three step to configure MDaemon at LAN:
Setting Primary Domain
First step of server mail configuration is to make domain for the account of E-Mail in network. Because you will only using it in local network which not connected to the internet, hence you can make to the name of domain freely without needing registration to Internic and also other registration.
- Open the Main Window of MDaemon, then Setup -> Primary Domain.
- Domain Name: (fill with organization domain)
- HELLO Domain: (name of domain which [is] used in SMTP instruction HELLO/ehlo in process delivery of E-Mail.)
- Machine Name: (Domain Name)
- Domain IP: (Computer IP at Local Network)
- Bind listening sockets to this IP only: (Leave it blank for single Domain, usually this fill use for multiple domain)
- ISP or Smart host’s IP or domain name: (Leave it blank for E-mail at LAN)
- Full Name: filled with complete name of user
- Mailbox Account: Filled with name to be used as E-Mail address
- Allow this account to be accessed with POP/IMAP mail clients: is used to give rights so that the account can be accessed from POP client /IMAP like Outlook and Eudora.
- Account password: Password for the account.
- Comments on this Account: Column to fill in various note lionized for the account.
- Message directory: location of directory path where E-Mail keep
- Storage Format: representing depository format of file in folder for every user.
- Enable automatic extraction of MIME encoded attachments: if this choice is activated, MDAEMON will extract E-Mail attachment which have found by MIME format to every E-Mail which enter. This facility is used especially for the client of E-Mail which do not have ability of MIME file extract.

Domain/ISP is a main tab of Primary Domain Configuration that contain of Primary Domain Server mail. Fill the form as below:
Other fill using for WAN email account purposed.
Create Account Mail
Create Account to be used in LAN environment and internet use menu and way of which is same. An account can relate to internet hence must be done some configuration according to delivery method and selected acceptance.
For LAN purposed, create the account and password determine to the domain only.
To create the account choose Account -> New Account.

Stuffing configuration for the tab of Account shall be as follows:
To see mailbox tab content click Mailbox at Account Editor menu.
Mailbox configuration conducted to every account. This shares function to determine depository location of E-Mail every user in server MDAEMON before downloaded by pertinent user.

The Menu Mailbox content shall be as follows.
Steps to conduct MDAEMON configuration for internet connection shall be as follows:
- Modem Configuration, DialUp Networking to ISP, RAS DialUp/DialDown in MDaemon.
- DNS Configuration.
- Sending Email Configuration.
- Receipt Email Configuration.
- Enable RAS dialup/dialdown engine: To activation Dialup function.
- Make this many attemps to establish a session: Is used to determine how many times MDAEMON repeat dial to ISP.
- After dialing, wait this many seconds for a valid connection: This shares determine how long MDAEMON await to get link to ISP
- Connection persistence: you can decide MDAEMON will continuously
connect, or determined by] certain time interval (in minute) before finally MDAEMON disconnect with ISP, if there is no activity. - Use any currently active dialup session: To determine what is MDAEMON will use conection which is active to deliver of and acceptance of E-Mail,
so that no need to dial. - Logon name: Filled with got account from your ISP.
- Logon password: Password for the logon to ISP.
- Use this RAS dialup profile: Is available internet connection type choice combo box. This box present networking dialup choice as according to internet connection which have installed in Windows.
- If ISP or hosting web do not provide DomainpPOP facility and also ETRN.
- MultiPOP using as ETRN and DomainPOP
- You wish free E-Mail service host in MDAEMON, so that user in network do not
need connection to internet to get the E-Mail.
The configuration as follows:- Enable MultiPOP mail collection for this account: to activate MultiPOP function
- Server: POP3 server name - got from ISP
- Logon: User account in POP3 server
- Password: Password in POP3 server or APOP shared secret
- Use APOP (password field contains shared secret: Make this active if authentication password is APOP
- a copy of message on POP server: Keep the E-mail in POP3 server even MDaemon already downloaded, later you can read your mail from other location.
- messages once [xx] or more have accumulated (0 = never): Maximum Email keeping in POP3 server
- download messages larger than [xx] kb (0 = no limit: The limit of E-Mail size download.
RAS DialUp/DialDown
Before doing configuration at this session, we have to check: Modem already installed and DialUp connection to the ISP via Internet has been installed and running well.
For Setting RAS DialUp at MDaemon with press F7 or Setup -> RAS Dialup/dialdown.
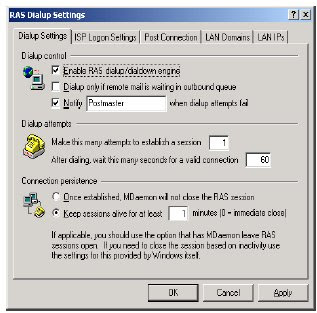
Dialup Setting Tab and ISP Logon Setting is a main menu must enter for MDaemon connected to the Internet. At Dialup tab setting there are some configuration type as follows:
The other Important things for RAS Dialup Settings menu is containing ISP Logon Settings tab of information concerning ISP account.
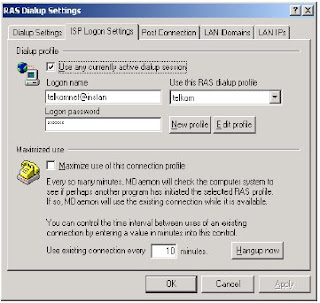
Configuration type in this shares shall be as follows:
DNS Configuration
Besides usage of Primary Domain which enlist, also need DNS configuration, MDAEMON use for look domain address in internet.
Configuration of DNS conducted from DNS tab at Primary Domain configuration menu.

DNS number got from your ISP.
Sending E-mail using SMTP Relay
This method using your ISP SMTP server or hosting Mail as a relay machine to the Internet. (same parameter with MDaemon on LAN, except: the ISP smart host 's IP or domain name with your SMTP ISP Server, then choose Send every outbound email message to this host).

Receive E-mail using MultiPOP
E-Mail address is usually equiped by POP3 facility for download of E-Mail from server to client like Outlook and Eudora. In MultiPOP Outlook role method as E-mail client replaced by MDAEMON later on distribute the E-Mail to every user.
MultiPOP can use as following:



